iDCP e-Invoice Software System
Certified E-Invoice Solution in Malaysia
- 100% LHDN and Peppol network compliance
- API Middleware service
Automated E-Invoices for Malaysian Businesses

Support B2B B2C e-Invoicing
Create and submit invoices instantly to LHDN with just a few clicks. Easily generate, send, and monitor e-Invoices directly from iDCP ERP and POS systems. No more manual uploads.

Handles all e-Invoice Format
Whether it’s standard, self-billed, consolidated, credit note, debit note, or refund — we’ve got you covered. Handle submissions, validations, and adjustments without stress.
Real-time e-Invoice Status
Monitor every e-invoice status in real time, draft, submitted, validated, or cancelled, and filter by invoice type, date, location, customer, and vendor.
Key Facts About Malaysia's e-Invoice Implementation
What is the e-Invoice implementation timeline in Malaysia?
The e-Invoice implementation in Malaysia rolls out based on annual turnover or revenue thresholds:
1. Businesses with revenue over RM100 Million must comply by August 2024
2. RM25 Million - 100 Million by January 2025;
3. RM5 Million - 25 Million by July 2025;
4. RM1 Million - 5 Million by January 2026.
*Less than RM1 Million revenue are exempted from the e-invoice implementation. (Updated 7 December 2025)
What are the requirements for e-Invoicing in Malaysia?
e-Invoices must cover B2B, B2C, and B2G transactions in UBL 2.1 (XML/JSON) format, include 55 mandatory data fields, and be submitted via the MyInvois Portal or through API integration.
What are the types of e-Invoices in Malaysia?
- Standard Invoices – for B2B, B2C, and B2G transactions
- Consolidated e-Invoices – for grouping low-value B2C sales. From Jan 1, 2026, transactions above RM10,000 must have individual e-Invoices; consolidated ones won’t be allowed.
- Self-Billed e-Invoices – for cross-border or unregistered suppliers.
What are the real-time validation requirements?
The IRBM will validate invoices in real-time, generating Unique Identification Numbers (UIN) and QR codes. Businesses will have a 72-hour window to reject or cancel invoices.
What if my invoice currency is not MYR?
Effective September 1, 2025, if your invoice’s currency code is not MYR, your e-Invoice payload must include the Currency Exchange Rate element.
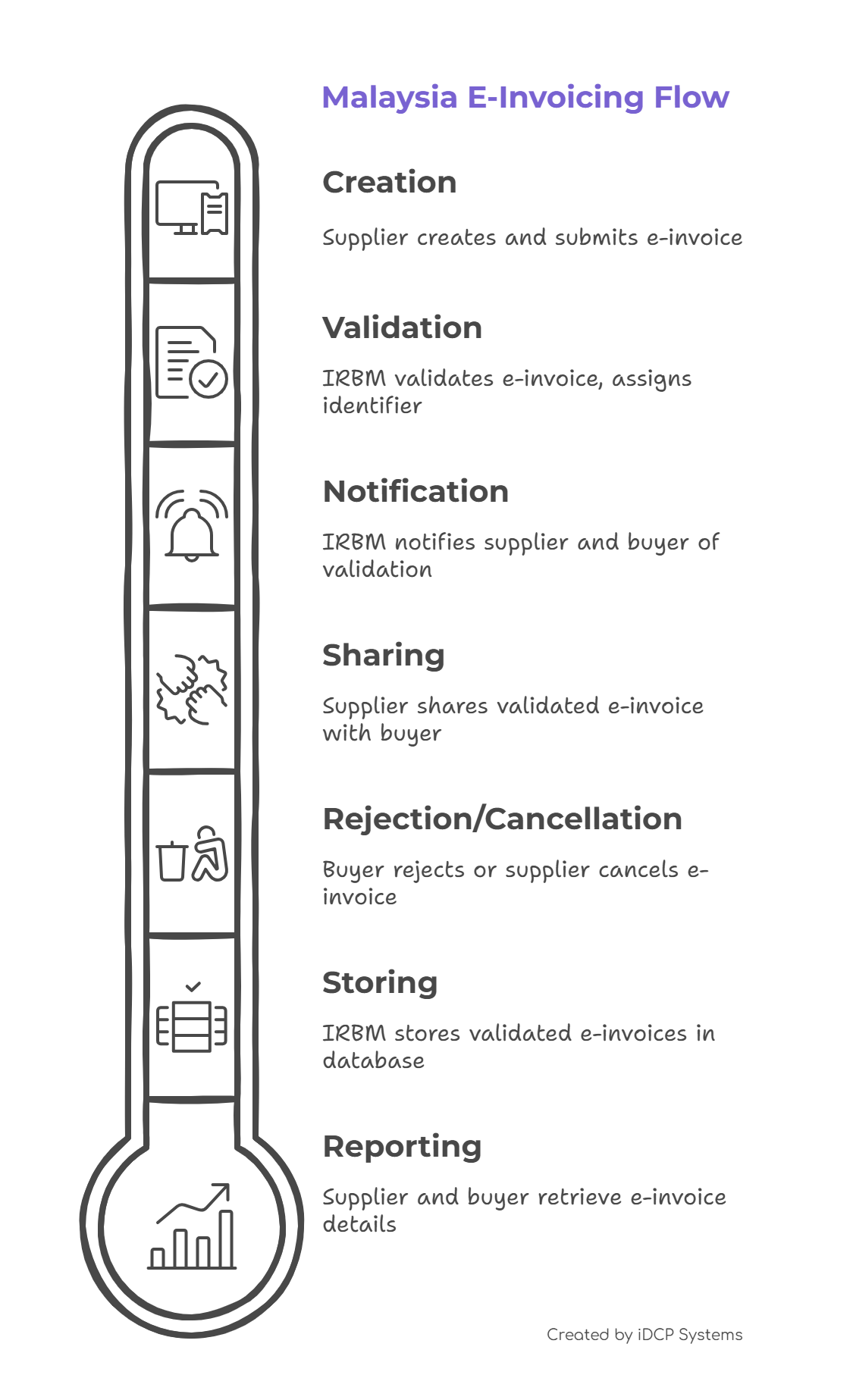
The Differences Between B2B and B2C e-Invoicing Transactions

B2B e-Invoicing Transactions
- Issuance: The supplier creates and submits an e-Invoice to IRBM via the MyInvois Portal or through a business system integrated with the MyInvois API.
- Validation: IRBM validates the e-Invoice in real time and issues a Unique Identifier Number (UIN).
- Notification: Both the supplier and buyer receive notification of the validated e-Invoice.
- Sharing: The supplier shares the validated e-Invoice with the buyer, including a QR code.
- Rejection or Cancellation: Within 72 hours, the buyer may request a rejection and the supplier may cancel the e-Invoice. Any rejection or cancellation must be supported with justification.
- Human-Readable Format: Suppliers may also provide buyers with a human-readable version of the e-Invoice (e.g., PDF or JPG).
B2C e-Invoicing Transactions
- When the Buyer Requests an e-Invoice: The supplier collects the buyer’s details and generates the e-Invoice in real time, following the same process as B2B.
- When the Buyer Does Not Require an e-Invoice: Seller issues normal receipt. IRBM permits seller to consolidate these transactions into a monthly consolidated e-Invoice. *Consolidated e-invoices allowed until 31 December 2025.
iDCP e-Invoicing Solutions
Choose the Solution
All-In-One
E-Invoice ERP
System
LHDN & MDEC Approved
Direct API sync with MyInvois
Real-time Validation
Auto UUID & QR Code Retrieval
Finance & Accounting Sync
B2B B2C e-Invoice Portal
Live status tracking
POS system e-Invoice receipt
API Middleware Service
Integration to ERP & POS
Multi-API support
REST API, OData API, SOAP API and Custom APIs
Sync master database
Real-time dashboards
Real-time status tracking
UUID & QR Code Retrieval
Accurate tax reconciliation
Benefits of iDCP e-Invoicing
Streamlined Operations
Automates invoice processes and reduce manual work.
Improved Cash Flow
Accelerates payments and reduces billing disputes.
Enhance Tax Compliance
Ensure efficient and accurate tax reporting.
Simplified International Trade
Facilitates cross-border business transactions more easily.
Cost Savings
Reduces paper usage and compliance costs.
Scalability
Support for current and future e-invoice transactions volumne.
Book a Free Demo
Get started today and experience the power of iDCP e-Invoice Solution - built for modern businesses.
Contact Us
Thank you for your interest.
We will get in touch with you ASAP.
Please try again later.
FAQs
-
How far has Malaysia progressed with e-invoicing implementation?
E-invoicing is being rolled out in phases and is now compulsory for a significant segment of businesses.
By July 2025, companies with annual revenue exceeding RM 25 million are already required to issue e-invoices in B2B, B2G, and B2C transactions.
Beginning 1 July 2025, the mandate will expand to include businesses whose annual turnover exceeds RM 5 million.
The rollout will proceed in stages until it covers all companies — with the exception of those whose annual turnover is under RM 1,000,000. (Updated 7 December 2025)
-
How does iDCP’s e-invoicing solution work?
iDCP automates the entire e-invoicing process:
- Integration: Connects to your ERP or business systems.
- Data Capture: Extracts invoice information.
- Formatting: Converts data into UBL 2.1 (XML/JSON).
- Validation: Submits for real-time verification with IRBM’s MyInvois system.
- UIN & QR Code: Receives and attaches the Unique Identification Number and QR code.
- Delivery & Storage: Sends e-invoices to buyers and archives them for compliance.
-
What are the e-Invoicing submission methods in Malaysia?
There are two ways to submit e-Invoices:
MyInvois Portal – Manual entry or bulk spreadsheet upload, ideal for MSMEs or low-volume transactions.
API Integration – Direct ERP or accounting system connection for real-time, automated submissions, supported by LHDN’s SDK.
-
What are the benefits of e-invoicing for businesses in Malaysia?
E-invoicing helps businesses streamline operations and maintain compliance:
- Streamlined Operations: Automates invoicing, reducing manual errors.
- Faster Payments: Improves cash flow and minimizes billing disputes.
- Better Tax Compliance: Simplifies and ensures accurate reporting.
- Lower Costs: Cuts paper and administrative expenses.
- Supports Global Trade: Facilitates cross-border transactions.
-
What are the steps to start e-Invoicing in Malaysia?
To begin with e-Invoicing in Malaysia, start by assessing your company’s readiness. Identify whether e-Invoicing is mandatory for your business or if you plan to adopt it voluntarily. Review your existing ERP or accounting system to confirm its compatibility and integration capability. Lastly, make sure your employees are properly trained to manage e-Invoicing processes efficiently.
-
What are the key features of iDCP’s e-invoicing software for Malaysia?
iDCP provides a comprehensive, MDEC-accredited e-invoicing solution designed for Malaysian businesses:
- Seamless Integration: Connects easily with ERPs and business systems.
- Multi-Channel Support: Consolidates B2B and B2C sales into compliant e-invoices.
- Client Portal: Enables buyers to generate e-invoices independently through a web or mobile platform.
- Real-Time Validation: Ensures compliance with IRBM’s MyInvois system.
-
What is an e-Invoice?
An e-Invoice (electronic invoice) is a digital document that records the details of a transaction between a seller and a buyer. Unlike traditional paper invoices, it is created, validated, and stored electronically through the LHDN MyInvois system.
Example: When a wholesaler sells goods to a retailer, instead of issuing a paper invoice, they generate an e-Invoice through their ERP /accounting system, which is then sent to LHDN for validation before being shared with the buyer.
-
What is a Credit Note?
A credit note is issued by a seller to correct a previously issued e-Invoice, usually to reduce the original invoice’s value without returning money to the buyer. It is commonly used to fix errors, apply discounts, or account for returned items.
Example: A retailer returns 20 defective shoes from an order of 200 pairs. The supplier issues a credit note to reduce the invoice value accordingly.
-
What is a Debit Note?
A debit note is issued to record additional charges or costs related to a previously issued e-Invoice.
Example: A supplier realizes that delivery charges were left out of the original invoice. They issue a debit note to add the extra cost.
-
What is a Refund Note?
A refund note (refund e-Invoice) is issued by a seller to record a refund given to the buyer.
Example: A buyer cancels an order and requests a refund. The seller issues a refund note to document the repayment.
Remark: According to LHDN rules and regulations, any cancellation of an e-Invoice must be done within 72 hours from the time of issuance.
-
What is a Self-Billed e-Invoice?
A self-billed e-Invoice is created by the buyer instead of the seller. It applies in situations like transactions with unregistered suppliers or cross-border dealings.
Example: A Malaysian retailer purchases raw materials from a foreign supplier not registered with LHDN. The retailer issues a self-billed e-Invoice to record the transaction.




